Addressing the Needs of the Growing Population of ELLs in Today’s Classrooms
As classrooms across the country continue to welcome a rising number of English Language Learners (ELLs), teachers face the challenge of ensuring that all students receive equitable learning opportunities. ELL students are not only tasked with learning academic content, but must also simultaneously acquire a new language. This dual challenge can create barriers to success in the classroom, making it crucial for educators to develop strategies that support both content mastery and language acquisition. Understanding this complexity is key to creating an inclusive learning environment where all students can thrive.
7 Essential Elements for Supporting ELLs in the Classroom
To address this challenge, our sister company, IDE Corp., has partnered with schools to support educators by helping them implement the 7 Essential Elements for supporting ELL students. These elements — physical space, scaffolding, resources, explicit language instruction, facilitation, emotional wellness, and social engagement — are designed to create a comprehensive learning environment that supports language development alongside academic growth. These essential elements provide a roadmap for educators to create inclusive, supportive, and effective learning environments for ELL students.
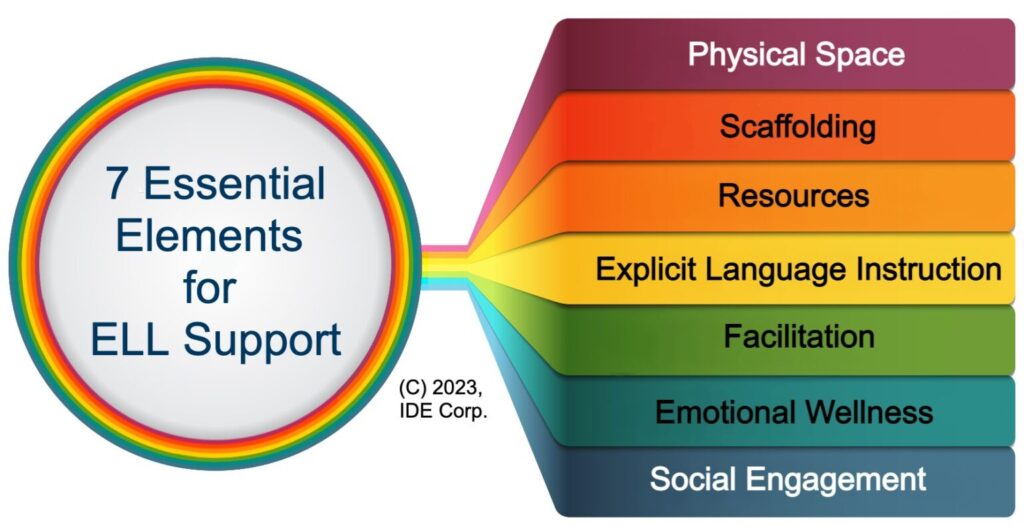
- Physical Space — Create a welcoming, affirming, and supportive classroom environment, whether physical or virtual. Label classroom items and display anchor charts to reinforce English language use. Celebrate the heritage of your ELLs by featuring flags or notable figures from their native countries. Use a word wall with subject-specific terms, translated when possible. Ensure that expectations and procedures are clearly visible, so students can easily follow along. Arrange the space to encourage peer collaboration and interaction.
- Scaffolding — Provide supports to help students successfully engage with the work. Use visuals to assist with vocabulary comprehension, and emphasize action words in instructions to make tasks clearer. Depending on the students’ English proficiency, offer summaries of complex texts. Ensure that videos include closed captions, and provide audio versions of written content. Offer sentence starters and frames to guide both written assignments and classroom discussions.
- Resources — Whereas scaffolding involves teacher-provided supports, resources are tools students can access independently. Examples include cognate lists (words that sound and mean the same in both languages), Hi-Lo books (high-interest, low-vocabulary texts), visual dictionaries, graphic organizers, and optional sentence stems and frames to aid language development.
- Explicit Language Instruction — In addition to support from ENL teachers, classroom teachers can provide direct English language instruction. This could involve teaching phonology (sounds of the language), morphology (word formation), syntax (sentence structure), semantics (meaning), and pragmatics (language in context). Offering explicit instruction helps ELL students build their language skills more effectively.
- Facilitation — When students work independently or in small groups, it’s important to facilitate their learning process. Use questioning techniques that promote higher-order thinking, covering comprehension, application, connections, synthesis, and metacognition. Provide support in content, process, and language skills to help ELLs progress through lessons.
- Emotional Wellness — Create a supportive atmosphere that fosters confidence and resilience in your ELL students. Teach stress reduction techniques, and provide opportunities for students who share the same native language to discuss content in their own language for comfort. Respect the “silent period” in language learning, allowing students time to adjust without pressure to speak in front of the class. Offer alternatives such as graphics or images for self-expression, and ensure that students have time to practice before sharing. Building strong relationships with your students is key to helping them feel comfortable in your classroom and more willing to engage in challenging academic tasks.
- Social Engagement — Provide ample opportunities for students to interact with their peers in collaborative settings where they can listen, speak, read, and write about the content. Language acquisition is often easier when students engage with classmates in informal settings, which can feel less intimidating than teacher-led instruction. Peer interaction is a vital part of language development, allowing students to practice their new skills in a supportive environment.
Strategies for Supporting ELLs: A Professional Learning Experience for Educators
To further support schools and districts, we as educators have created a resource for educators that provides the necessary tools and instructional strategies to help ELL students thrive. Our online Professional Learning Experience (PLE) resource titled Strategies for Supporting ELLs is designed to equip teachers with practical strategies aligned with the 7 Essential Elements. This PLE empowers educators to implement instructional techniques that make a meaningful difference in ELL students’ academic success and language development. Check out the sample image below that shows some of the learning that takes place in one of the modules on Providing Resources for Student Self-Advocacy. By providing ongoing professional development, Strategies for Supporting ELLs helps schools foster an environment where teachers are prepared to meet the evolving needs of their diverse student populations.
Support Across All Content Areas
Our PLE doesn’t just focus on general strategies — it offers targeted support and resources for integrating ELL instructional strategies across content areas. In math, scaffolding and visual supports help ELLs understand abstract concepts and solve problems. For ELA, explicit language instruction is key to helping students develop literacy skills in English while also analyzing literature and constructing essays. In science, inquiry-based learning can be adapted to support language development, with emphasis on vocabulary acquisition and interactive experiments. Finally, in social studies, our strategies enable ELLs to engage with complex historical texts and discussions, promoting both content understanding and critical thinking. Supporting ELLS in all content areas ensures that educators can meet the language and content needs of their ELL students, no matter the subject matter. For other strategies for success, check out our blog that supports ELLs in all content areas. The image below is a sample of a downloadable, ready-to-use resource that comes from our PLE. It provides sentence stems to support ELLs in all content areas.
Contact Us to Learn More About Supporting ELL Students
As the ELL population continues to grow, schools must be prepared to support these learners effectively. Our Strategies for Supporting ELLs PLE is a valuable resource that helps educators foster a culture of professional learning designed to meet the needs of ELL students. If you’re looking for a PD experience facilitated by a consultant, try out our Virtual Learning Communities that offer 25 hours of targeted ELL support. Contact us today to speak with one of our experts and learn how you can implement these resources in your school or district to support the academic and language development of your ELL students. Together, we can ensure every student has the opportunity to succeed!


 In this course, participants will leverage choice and technology to provide students with the ultimate differentiated learning environment. They will develop differentiated digital activity lists rooted in rigorous instruction that offer multiple ways to learn and apply content. Participants will explore autonomy, purpose, and mastery as motivators in all learning environments. They will design differentiated activity lists to put students in charge of their own learning, creating a structure that allows students to make decisions within a structured framework. Making informed decisions is an essential life skill that teachers can support with intentional classroom practices.
In this course, participants will leverage choice and technology to provide students with the ultimate differentiated learning environment. They will develop differentiated digital activity lists rooted in rigorous instruction that offer multiple ways to learn and apply content. Participants will explore autonomy, purpose, and mastery as motivators in all learning environments. They will design differentiated activity lists to put students in charge of their own learning, creating a structure that allows students to make decisions within a structured framework. Making informed decisions is an essential life skill that teachers can support with intentional classroom practices. Participants in this course will use Reinventing the Classroom Experience by Dr. Nancy Sulla as a resource. The assigned book must be
Participants in this course will use Reinventing the Classroom Experience by Dr. Nancy Sulla as a resource. The assigned book must be